 Data is a valuable asset for anyone so taking regular backups is important to secure it from any unforeseen data loss.
Data is a valuable asset for anyone so taking regular backups is important to secure it from any unforeseen data loss.
While individual users use external hard drives or cloud-based services to create data backups, this is not really a viable option for enterprises and large-scale business units.
They need to opt for a storage solution, which is both robust and reliable. This is why they rely on RAID storage.
RAID or Redundant Array of Independent Disks is system of scalable storage solution used for storing data across multiple storage drives connected together. It is mainly used for protecting data in case of an unforeseen data loss and increasing data availability. It can be configured in various levels or configuration like 0, 1, 5, 6, 10 and more.
RAID 10 is one such example of RAID that we will discuss here. It is a type of nested RAID array that combines two types of RAID levels to meet user demands of data security. Even with RAID 10 bringing the mirroring capabilities of RAID 1 to the table, it is still prone to data loss due to many reasons, absence of parity being the most prominent.
Before moving onto RAID 10 recovery, let’s understand what RAID 10 is and how data loss occurs in it.
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10 is also known as RAID 1+0, is a type of hybrid or nested RAID that employs both data striping and mirroring techniques for storing data across the drives.
RAID 10 storage requires at least 4 disks configured in pairs or groups of 2. Drives in each group use data mirroring but the groups themselves use data striping. A simple depiction of RAID 10 array is in the diagram below:
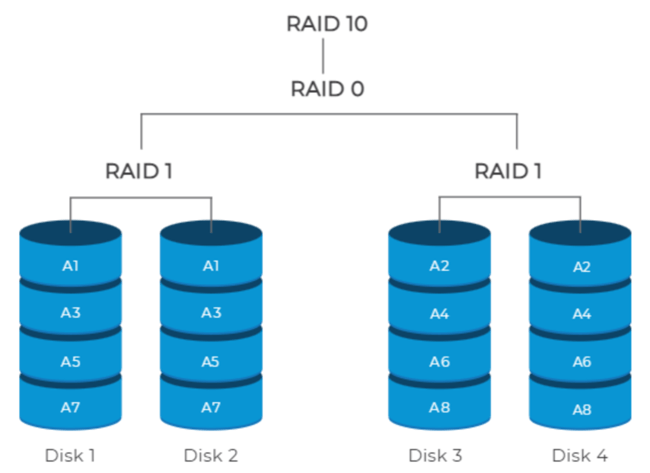
These 4 drives are grouped in pairs and each pair is configured at RAID 1 level. The two RAID 1 disk pairs are configured at RAID 0 level.
The data is stored across the pairs using data striping. As depicted in the diagram above, disk 1 and disk 3 are storing data in striped manner or in chunks, i.e., A1, A2, and so on.
Inside each group or pair configured at RAID 1 level, data mirroring technique is employed. The data present on disk 1 is replicated onto disk 2, and similarly, the data on disk 3 is replicated onto disk 4. In simple words, disk 2 and disk 4 are mirror copies of disk 1 and disk 3, respectively.
As RAID 10 consists of RAID 1 and RAID 0, the combination proves to be fast during reading or writing data. While this configuration provides increased data availability and high I/O write speeds, it lacks parity.
RAID 10 has a fault tolerance of 1 disk failure in case of mirrored sets. If one drive fails in that group, the data can be recovered from the active drive.
However, if both the disks fail, and there is multiple disk failure across the groups, the RAID 10 array will fail. In such a scenario, a third-party RAID data recovery tool might help recover data from a failed RAID 10 array.
Reasons for Data Loss in RAID 10
RAID 10 is known for providing enhanced data availability and read/write speeds. However, like RAID 0 and RAID 1, it lacks parity. Any storage device including RAID storage is susceptible to data loss due to many reasons. Here are some common reasons that cause data loss in RAID 10:
- Multiple disk failure
- Array disk failure
- Disk rebuilding process failed
- RAID controller malfunctioned
- Data corruption
- Accidental deletion
- Unexpected power loss
- DDoS attack
Methods to Perform RAID 10 Data Recovery
Now that we have learned about RAID 10 and the reasons behind data loss from it, let’s discuss some methods to recover lost data from array RAID 10.
When we talk about recovering lost data from a failed RAID 10 array, there are 2 possible scenarios:
- When one disk has failed (Single-disk failure)
- When both the disks in a pair have failed (Multiple disk failure)
Let’s discuss these two scenarios in detail…
Case 1: Single-Disk Failure
When there is a single disk failure in RAID 10 array, the failed disk goes in the degraded state. Though the RAID array remains functional, it is advised to stop using it and hot swap the failed disk with a hot spare disk. As soon as the hot disk is connected, the controller will automatically rebuild the disk and recover lost data onto the newly swapped disk.
If in case the hot disk is not available, you can replace it with a new drive and manually initiate the rebuild process to recover RAID 10 data. Here are the steps to perform this:
1 – Type iprconfig and run the utility.
2 – Choose Work with disk unit recovery option.
3 – Click on Rebuild disk unit data.
4 – Choose the disk/s that you wish to rebuild and press the Enter key.
5 – Press Enter to rebuild data and q to cancel the process.
Case 2: Multiple Disk Failure
Multiple disk failure in a RAID 10 array is a bit tricky as it depends on whether the disk failure has happened in the same mirrored set or different.
If one disk failure has happened in every group or pair, then the process for rebuilding and performing RAID recovery is the same as mentioned in the case of single disk failure.
However, if there have been multiple disk failures across the array, i.e., both the disks have failed in one or more mirrored sets, then the disk array’s status changes to Failed. If your RAID 10 array has failed, here is what you can do:
1 – Immediately stop using it
2 – Delete the existing disk array
3 – Replace the failed disks to recreate the disk array
Once this is done, you can then recreate the file systems on the rebuilt disk array and copy all the data onto it from a backup drive to recover RAID 10 data from failed RAID and secondary disks.
Now that you have rebuilt the RAID 10, you still have the failed disks with data on them. You can also use a powerful RAID recovery software to recover data from such failed RAID drives.
A RAID data recovery software allows recovery of data from a failed RAID array. This tool can easily help users recover critical data from various failed RAID arrays including RAID 10. Such software are very capable and they use advanced RAID data recovery algorithms to easily find and recover data from a RAID array failed due to various reasons.
A RAID 10 recovery software can recover any type of file format from a failed RAID array or its degraded disks. It is also capable of performing data recovery from other storage devices like HDDs, SSDs, SD cards, optical disks, and more.
Final Words
RAID array is used where there is demand for high performance, data availability, and data security. RAID 10 is a nested array which combines two RAID levels, RAID 1 and RAID 0 to provide increased I/O speeds, data availability, and more. However, just like any other storage device, RAID 10 array too is susceptible to data loss due to various reasons.
It is a common notion that resolving RAID failures is challenging, which is true to some extent. However, performing RAID data recovery from a failed RAID array is rather simple. And if there is a powerful RAID recovery tool handy, then recovering data from a failed RAID becomes a cakewalk.